September 10, 2025
Neurovascular Response Modulation via Localized Cryo Applications
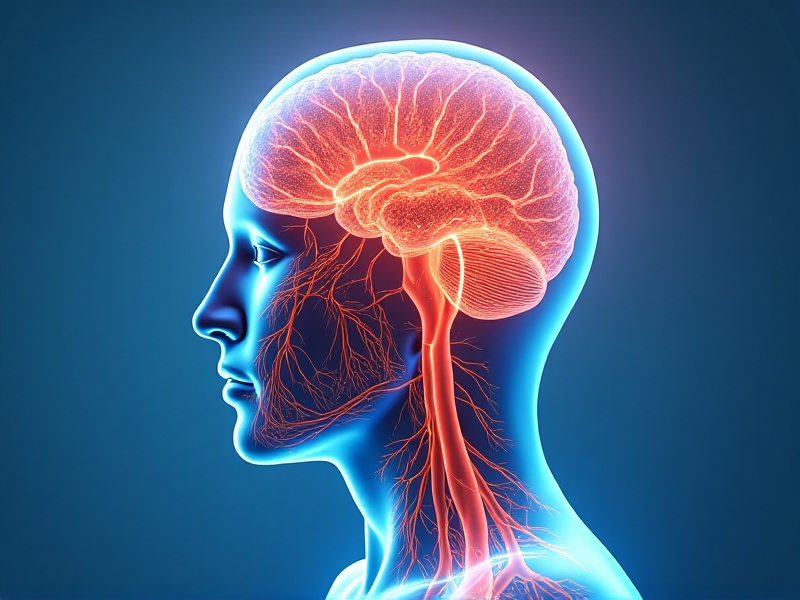
Understanding Neurovascular Response
The human body is a complex network of systems, with the neurovascular system playing a pivotal role in maintaining homeostasis. This system, which includes the nervous and vascular systems, regulates blood flow and neural activity in response to various stimuli. Understanding how these systems interact is crucial for developing therapeutic interventions, particularly in the context of localized cryo applications.
Neurovascular response refers to the body's ability to modulate blood flow and neural activity in reaction to external or internal changes. This can include temperature fluctuations, physical trauma, or even psychological stress. The primary goal of this response is to ensure that tissues receive adequate oxygen and nutrients while removing waste products efficiently.
Localized cryo applications, which involve the application of cold to specific areas of the body, have been shown to influence neurovascular response significantly. By understanding the mechanisms behind this interaction, researchers and clinicians can develop more effective treatments for a range of conditions, from acute injuries to chronic pain management.

The Science of Cryotherapy
Cryotherapy, the therapeutic use of cold, has been practiced for centuries, but its scientific underpinnings have only recently been fully explored. The application of cold can induce vasoconstriction, reducing blood flow to the affected area and thereby minimizing inflammation and swelling. This initial response is followed by a period of vasodilation, where blood flow increases, promoting healing and recovery.
Localized cryo applications, such as ice packs or cryo chambers, target specific areas of the body, allowing for precise control over the therapeutic effects. The temperature and duration of exposure are critical factors that influence the neurovascular response. Too much cold can lead to tissue damage, while insufficient exposure may not provide the desired therapeutic benefits.
Recent studies have shown that localized cryo applications can also modulate neural activity, reducing pain perception and improving overall function. This dual effect on both the vascular and nervous systems makes cryotherapy a versatile tool in the treatment of various conditions, from sports injuries to neurological disorders.

Mechanisms of Neurovascular Modulation
The mechanisms by which localized cryo applications modulate neurovascular response are complex and multifaceted. One of the primary pathways involves the activation of cold-sensitive receptors in the skin, which send signals to the brain to initiate a series of physiological responses. These responses include the release of neurotransmitters and the activation of the autonomic nervous system, which regulates blood flow and heart rate.
Another key mechanism is the reduction of metabolic activity in the affected area. Cold exposure slows down cellular metabolism, reducing the demand for oxygen and nutrients. This, in turn, minimizes tissue damage and promotes healing. Additionally, the release of anti-inflammatory cytokines helps to further reduce inflammation and swelling.
Understanding these mechanisms is essential for optimizing the use of localized cryo applications in clinical practice. By tailoring the temperature, duration, and frequency of exposure, clinicians can maximize the therapeutic benefits while minimizing potential risks. This knowledge also opens up new avenues for research into the use of cryotherapy in the treatment of chronic conditions and neurological disorders.
Clinical Applications of Localized Cryo Therapy
Localized cryo therapy has a wide range of clinical applications, from acute injury management to the treatment of chronic conditions. In sports medicine, cryotherapy is commonly used to treat sprains, strains, and contusions. The application of cold helps to reduce pain and swelling, allowing athletes to recover more quickly and return to their sport.
In the field of pain management, localized cryo applications have been shown to be effective in reducing chronic pain, particularly in conditions such as arthritis and fibromyalgia. The cooling effect helps to numb the affected area, providing immediate relief, while the reduction in inflammation promotes long-term healing.
Neurological conditions, such as multiple sclerosis and neuropathy, also benefit from localized cryo therapy. The modulation of neural activity can help to reduce symptoms such as pain, muscle spasms, and sensory disturbances. As research continues, the potential applications of cryotherapy in neurology are likely to expand, offering new hope for patients with these challenging conditions.
Future Directions in Cryotherapy Research
As the understanding of neurovascular response modulation continues to evolve, so too does the potential for new and innovative applications of localized cryo therapy. One area of particular interest is the use of cryotherapy in the treatment of cancer. Preliminary studies suggest that localized cold exposure may help to reduce tumor growth and improve the efficacy of chemotherapy.
Another promising direction is the integration of cryotherapy with other therapeutic modalities, such as physical therapy and pharmacotherapy. Combining these approaches could enhance the overall effectiveness of treatment, particularly for complex conditions that involve both vascular and neurological components.
Finally, advances in technology are likely to lead to the development of more precise and targeted cryo devices. These innovations could allow for even greater control over the therapeutic effects of cold exposure, opening up new possibilities for personalized medicine. As research continues, the potential for localized cryo therapy to improve health and well-being is vast, offering exciting opportunities for both clinicians and patients.